

The additional volume that can be expired below tidal volume is called the expiratory reserve volume, which is approximately 1200 mL. The additional volume that can be inspired above tidal volume is called the inspiratory reserve volume, which is approximately 3000 mL. With this maneuver, additional lung volumes are revealed. Next, the subject is asked to take a maximal inspiration, followed by a maximal expiration. Normal tidal volume is approximately 500 mL and includes the volume of air that fills the alveoli plus the volume of air that fills the airways. Normal, quiet breathing involves inspiration and expiration of a tidal volume ( V T). Residual volume cannot be measured by spirometry.įirst, the subject is asked to breathe quietly. Respiratory exchange quotient (CO2 production/O2 consumption)įigure 5–2 Lung volumes and capacities. Measurements of lung volumes and capacities are made by spirometry. Volume of forced vital capacity expired in 1 second
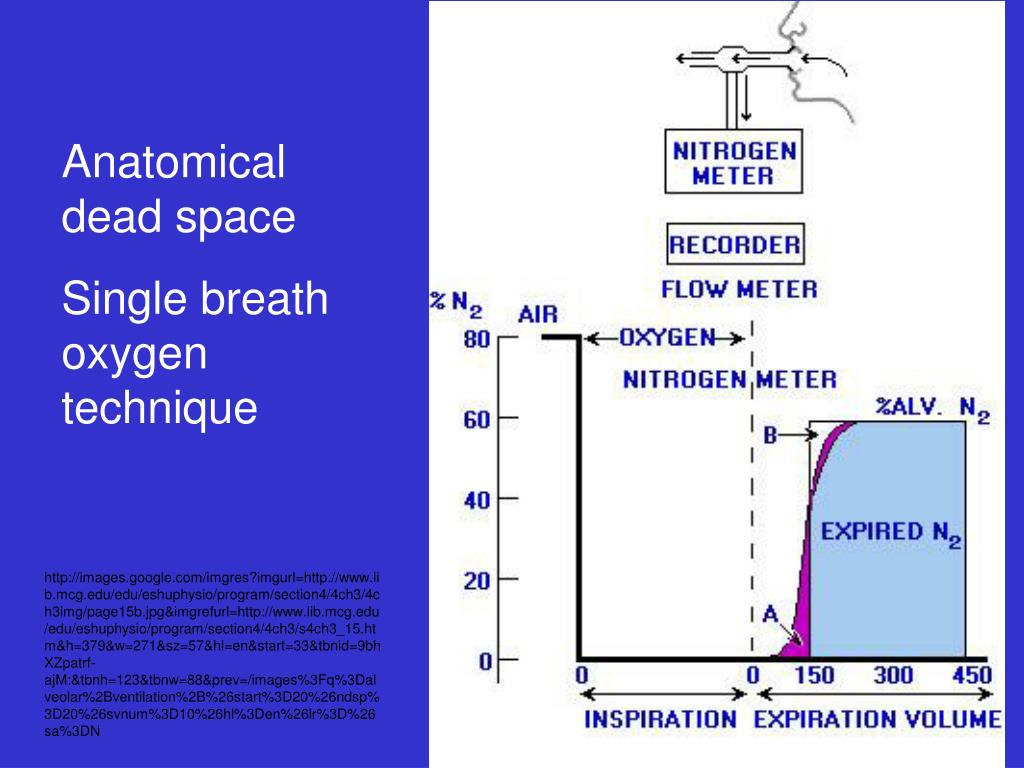
Partial pressure of CO2 in dry inspired air Partial pressure of O2 in dry inspired air Partial pressure of CO2 in arterial blood Table 5–1 Abbreviations and Normal Values Associated with Respiratory Physiology The volume displaced is recorded on calibrated paper ( Fig. Typically, the subject is sitting and breathes into and out of the spirometer, displacing a bell. Static volumes of the lung are measured with a spirometer ( Table 5-1).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
